Homepage / Applications / Precision cutting
LASER PRECISION CUTTING - SMALLEST KERFS AND CONTOURS
Laser cutting with modern CNC machines is one of the most variable, precise and dynamic cutting processes available today. Thanks to modern laser technology, almost all materials can be cut with high precision. There are almost no limits to the contours and geometries.
In addition to conventional sheet metal processing, the production of metallic and non-metallic precision parts such as thin foils or tubes is the most important area of application.
PROCESS - COMBINATION OF LASER BEAM AND PROCESS GAS
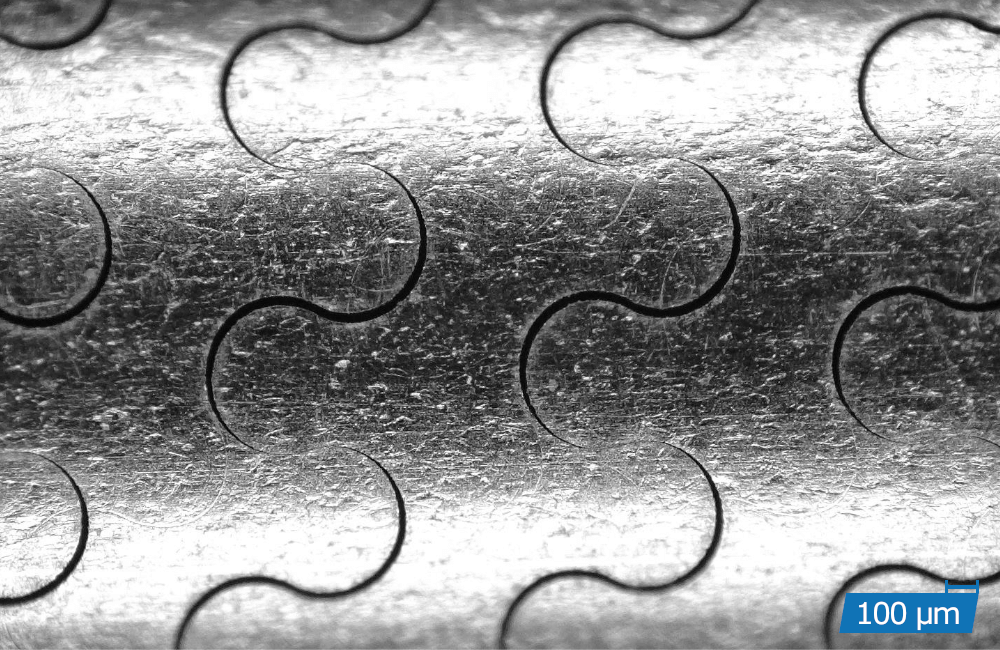
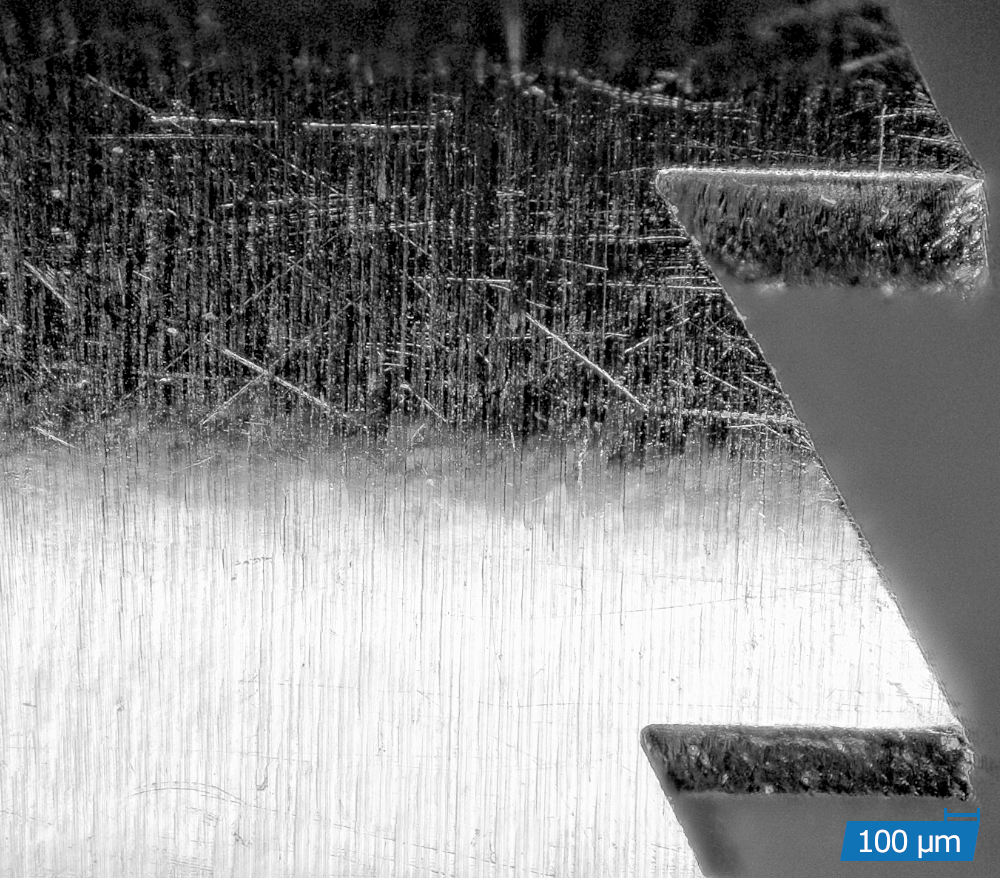
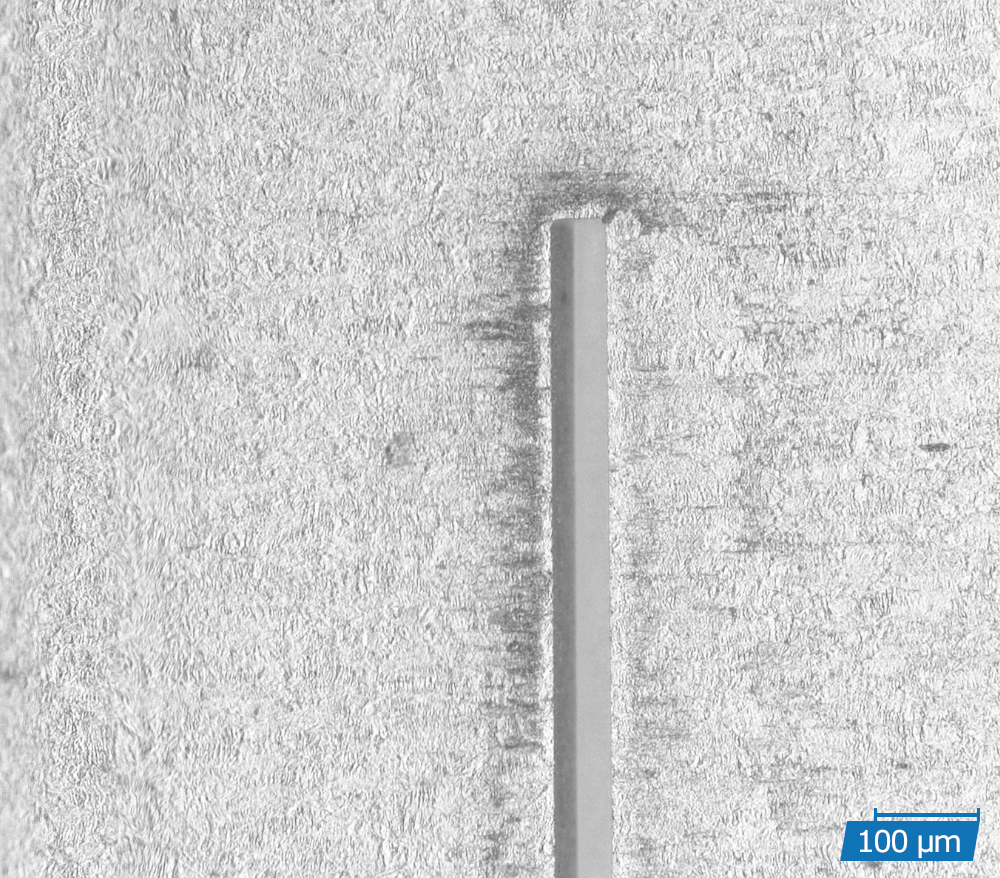
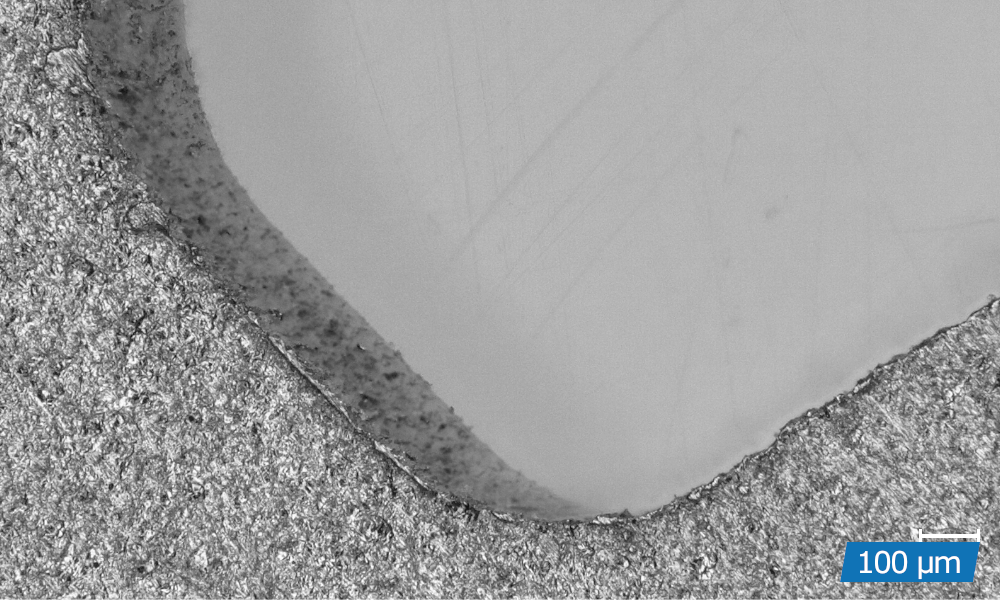
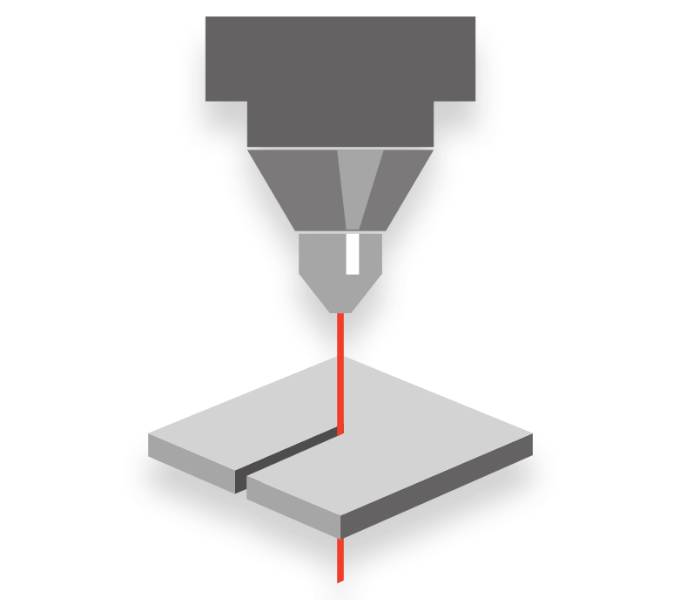
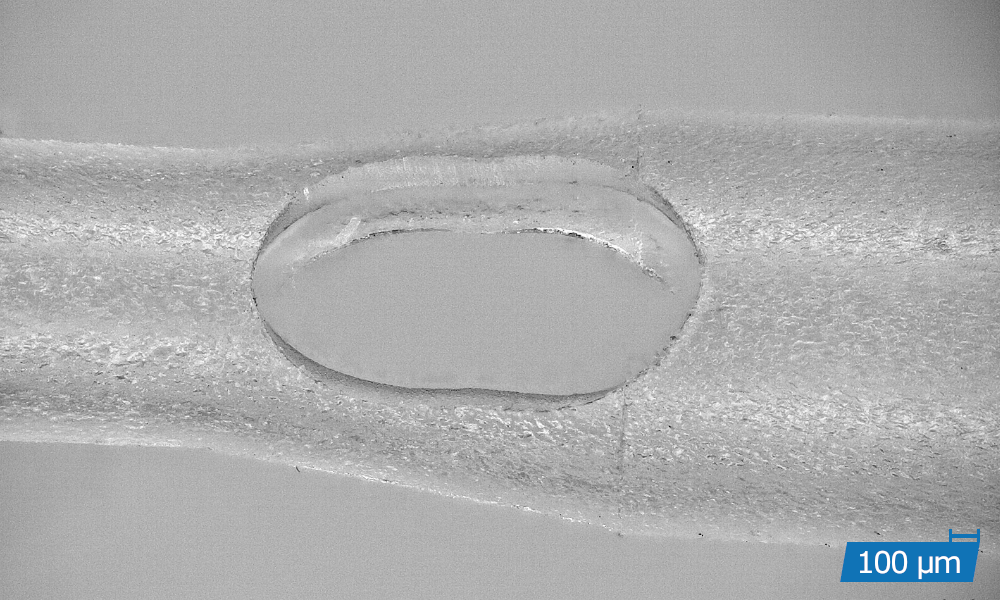
Precision cutting is a thermal cutting process in which a focussed laser beam combined with a coaxial process gas flow produces a very small cut. Through a relative movement between the laser beam and the workpiece, flat parts as well as tubes and three-dimensional contours can be realised with high precision and kerfs of less than 10 µm.
High-precision cuts with burr-free cutting edges
High dimensional accuracy and dimensional stability
No impact on the material properties
Machining of a wide range of materials
Cutting of complex geometries
Scope of Service
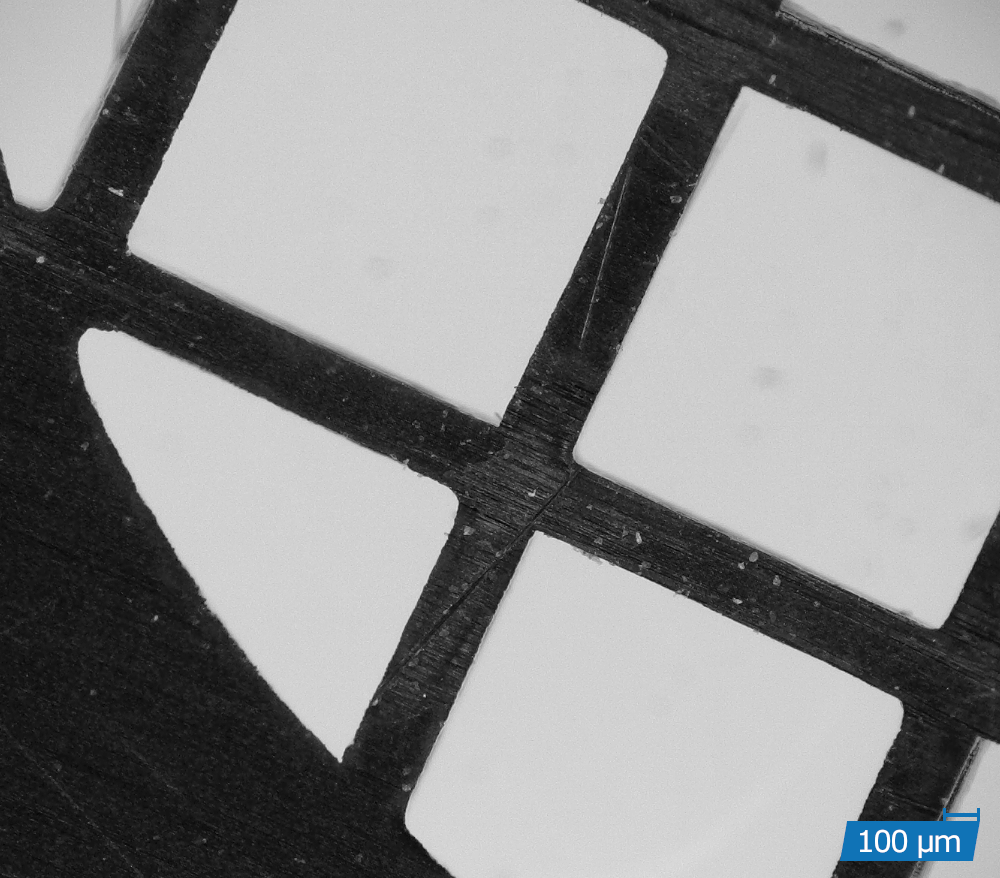
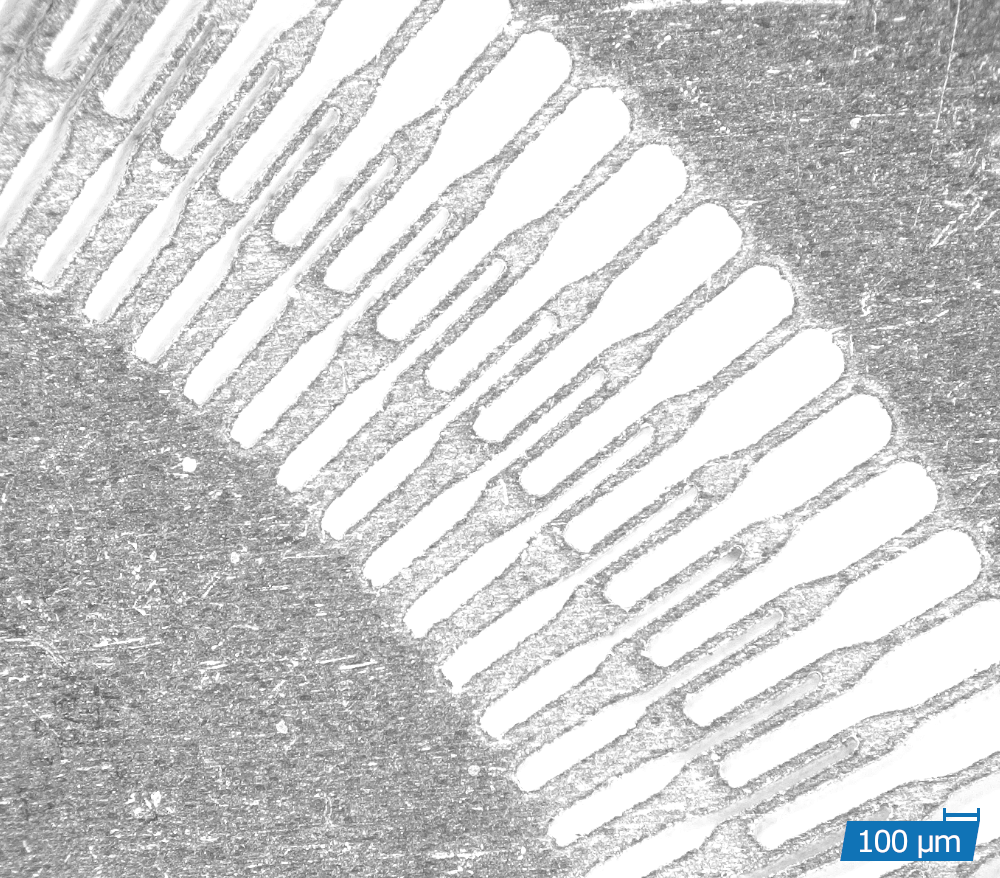
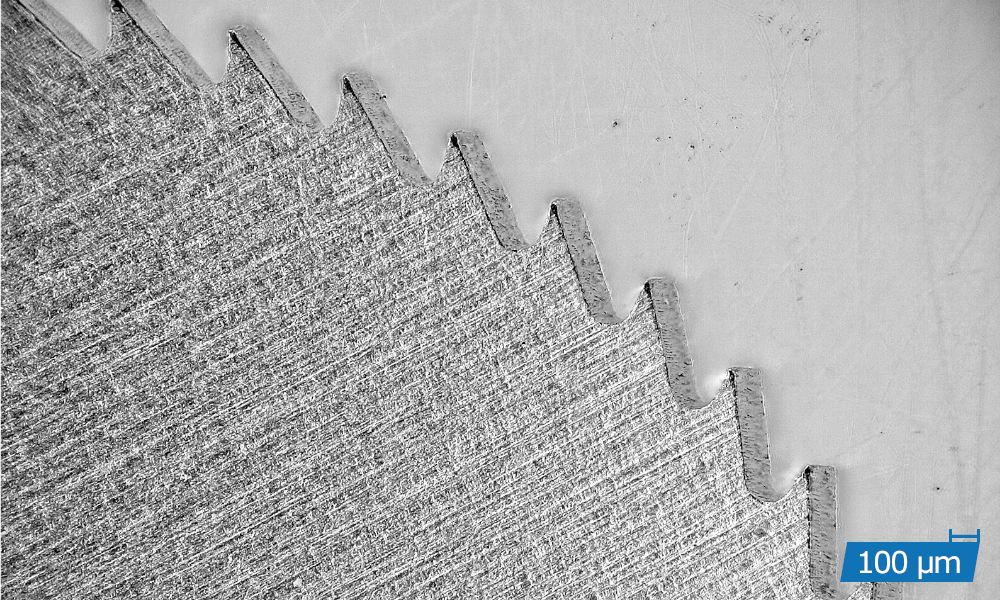
APPLICATION EXAMPLES
Flame cutting
Fusion cutting
Similar to flame cutting, a process gas is supplied during fusion cutting, the gas pressure of which also serves to blow the molten material out of the kerf.
It is not oxygen that is used to ignite the material. Instead, nitrogen or argon is used as a shielding gas.
The cutting speed is lower than with flame cutting. Oxidisation of the cut edges is avoided.
Sublimation cutting
Due to very short laser pulses, the material changes directly from a solid to a gaseous state during sublimation cutting without a molten phase. It evaporates or vaporises.
A shielding gas such as argon or nitrogen is also used in this process.
Sublimation cutting with ultrashort pulse laser technology generates only low thermal stress, which means that the material retains its desired properties and remains distortion-free.